Innovative plants enabling the sustainable recycling of Li-ion batteries
Primobius designs and builds recycling plants for lithium-ion batteries. Its advanced solutions enable customers to recover valuable materials from production scrap and end-of-life Li-ion batteries. Using eco-friendly technologies, the plants reclaim materials that might otherwise end up in landfills or be processed in less environmentally friendly ways. An efficient multi-stage process allows the recovery of critical raw materials from various battery chemistries, including lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) cathodes used in consumer electronics and nickel-rich lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) cathodes found in electric vehicles (EVs) and stationary storage applications.
Learn more on how Primobius empowers customers to recycle their batteries sustainably, recovering metals such as cobalt, nickel, lithium, and manganese in high purity. The reclaimed materials can be reintegrated into the Li-ion battery supply chain, supporting the circular economy and reducing reliance on primary resources.
Multi-step lithium-ion battery recycling process
Efficient recovery of critical materials
Primobius provides a patented recycling process and solutions that integrate components from partner companies to meet diverse customer needs. The process combines shredding and beneficiation with hydrometallurgical refining to achieve high-purity recovery of critical metals, helping industries reduce their reliance on primary raw materials. Our goal is to empower automotive OEMs, battery manufacturers, and recycling companies to close the loop in battery production. Customers can reintegrate recovered materials into their own supply chains or sell them, creating both environmental and economic benefits.
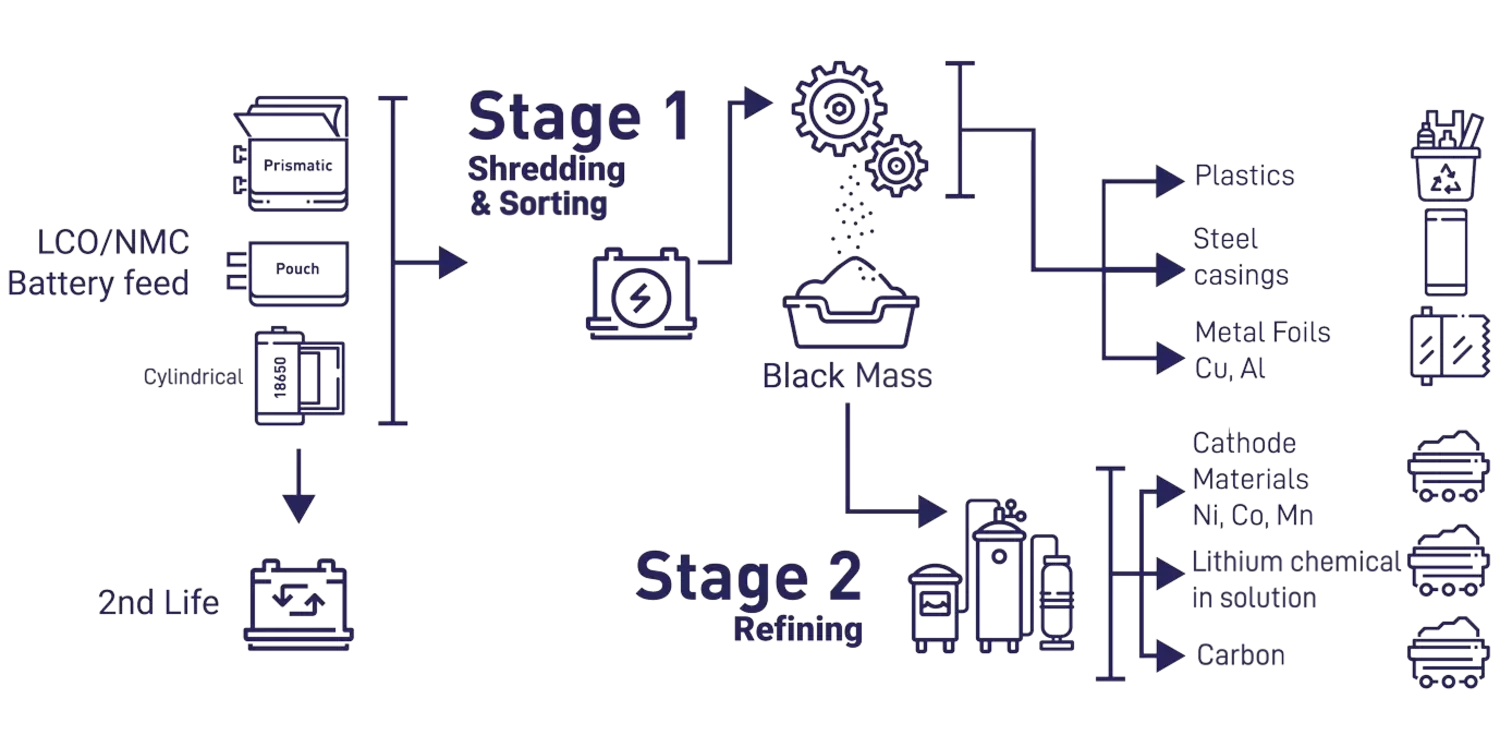
LiB recycling involves two core stages, each operated by separate plants:
- Shredding and beneficiation: This stage physically separates components, removing metal casings, electrode foils, and plastics from the main battery materials.
- Hydrometallurgical processes: This stage includes leaching, purification, and precipitation to predominantly produce refined chemical products via a specialized plant.
-
Feed preparation
The feed preparation process begins by determining whether battery modules require dismantling into constituent cells. This step ensures safe handling and processing of the batteries. Modules may also need to be discharged to a specified level to limit power before shredding, depending on their format and state of charge upon arrival.
![]()
-
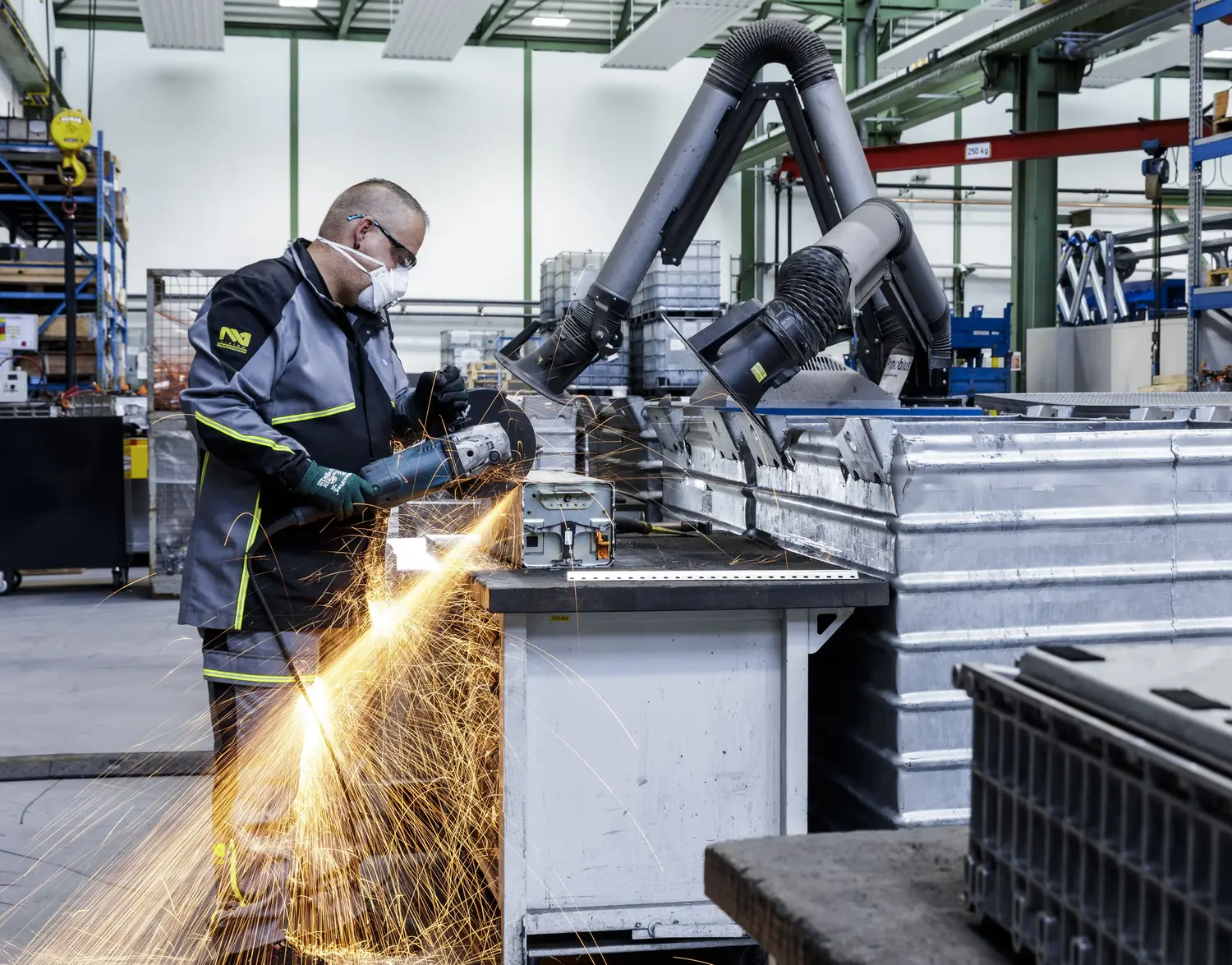
Shredding and beneficiation
The shredding and beneficiation stage processes spent batteries of various sizes, formats, and chemistries, including lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) cathodes from consumer electronics and nickel-rich lithium-nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) cathodes from electric vehicles and stationary storage applications. During shredding, plastic and metal components are separated from the "black mass," which contains the active materials of the battery.
The wet shredding process allows for the safe handling of partially discharged batteries. Multiple safety systems, including an inert gas environment, are used to manage fire risk during shredding. After shredding, drying and beneficiation further separate coarse plastic and metal materials from the feed. These recovered materials can be utilized in two ways: they may be sold as scrap to existing metal and plastic recyclers, providing an additional revenue stream, or they can be reintegrated into the customer's own battery supply chain, closing the loop and enhancing sustainability efforts.
The black mass produced in Stage 1 contains critical active materials such as lithium, nickel, and cobalt. These materials can be refined through hydrometallurgical processing in a separate plant. The refined chemicals are of high purity and suitable for reuse in battery cathodes.
![]()
-
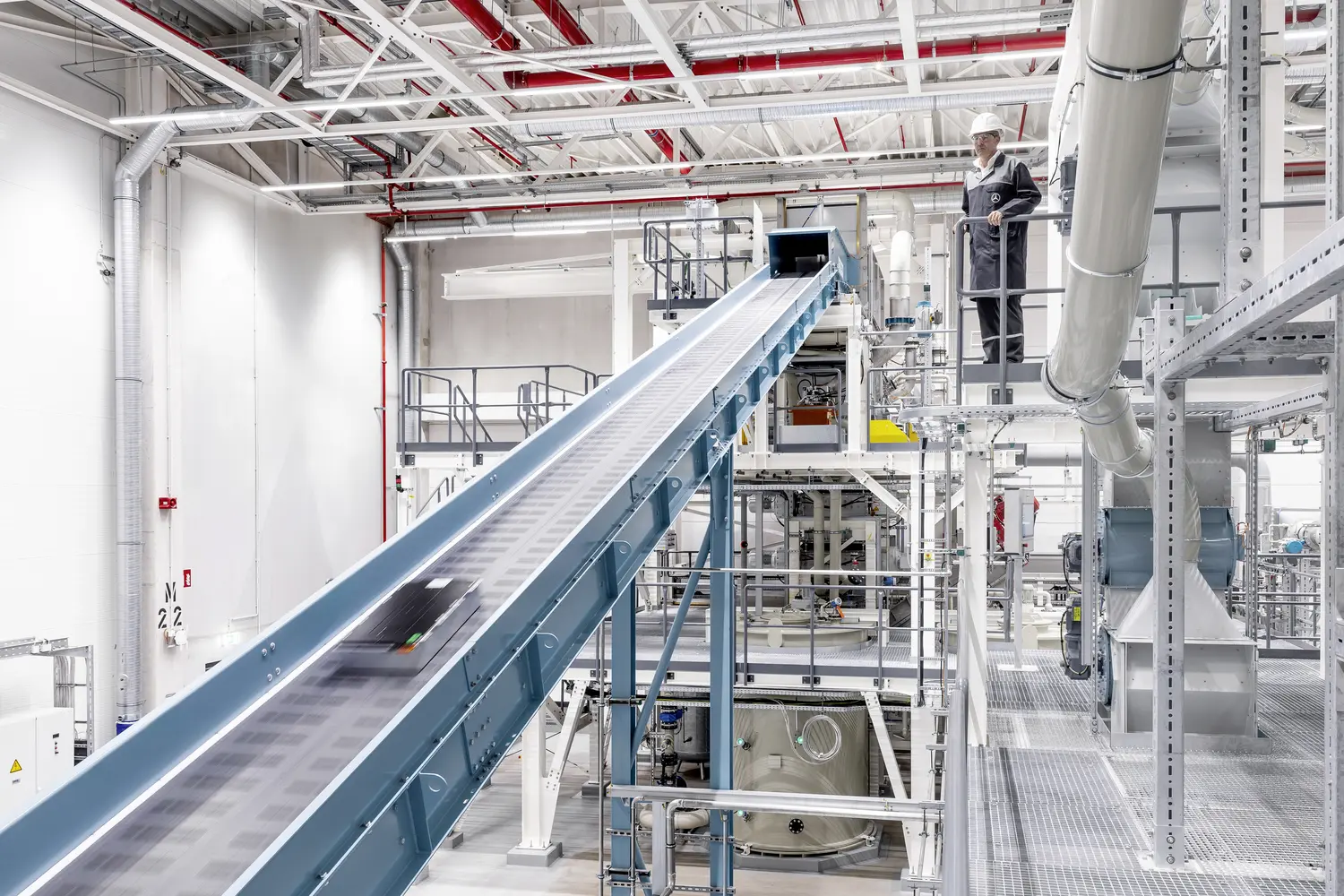
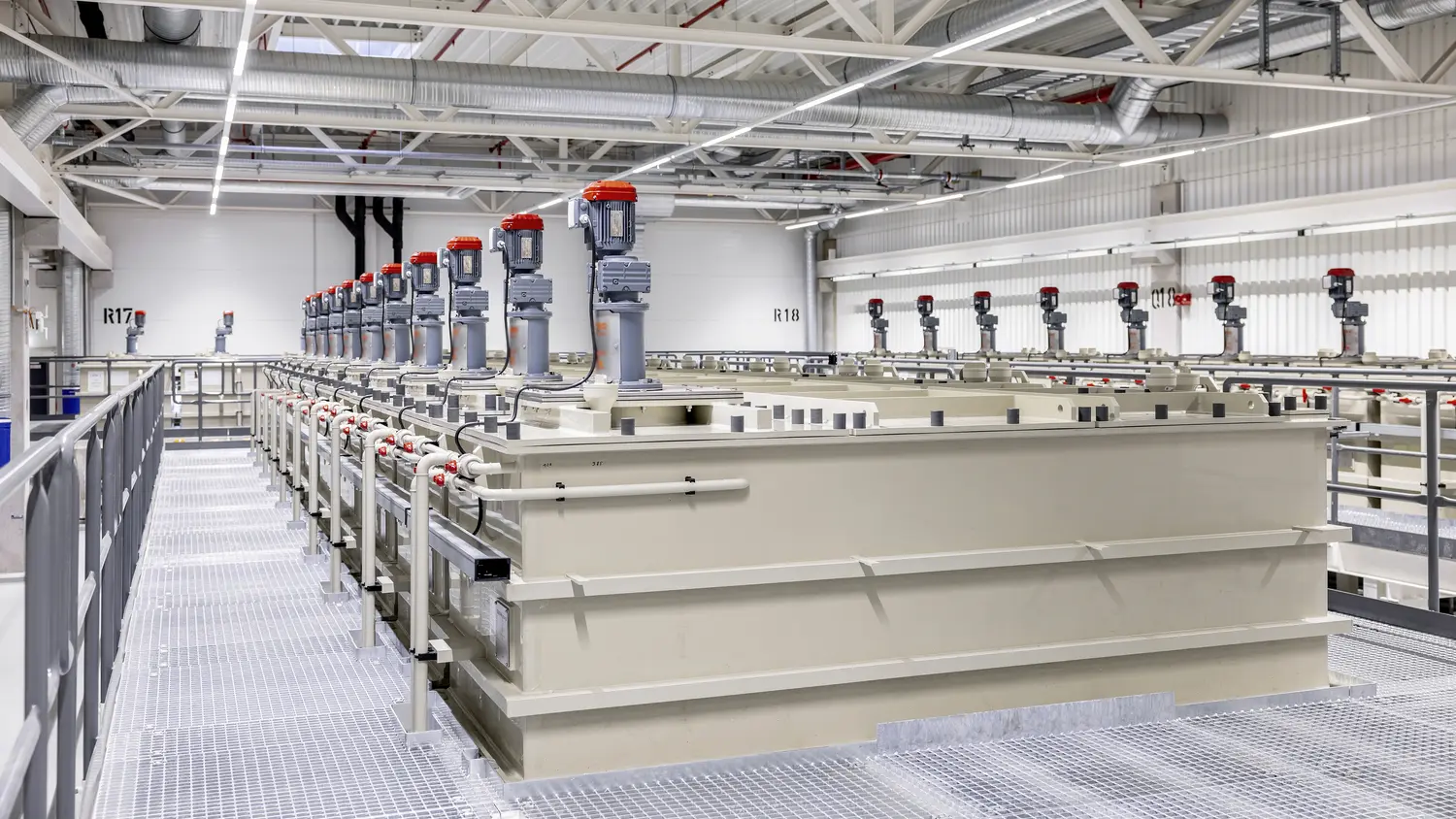
Hydrometallurgical processing
The second recycling stage processes black mass, which contains the active materials recovered during shredding and beneficiation. In the leach circuit, metals such as cobalt, nickel, manganese, copper, and lithium are extracted from the black mass. The pregnant leach solution (PLS) is separated from the solid leach residue, enabling further purification and recovery of valuable materials.
Cobalt and nickel are recovered as high-purity sulphates, which can be reintegrated directly into the lithium-ion battery supply chain for cathode manufacturing. Lithium is recovered as lithium sulphate, which can be converted into lithium hydroxide or lithium carbonate, both of which are essential for battery production.
The process also yields manganese and copper sulphates, which are suitable for sale to existing refineries or for direct industrial applications. The solid leach residue contains graphite anode material, which is dried and drummed for sale, offering customers flexibility in how they utilize recovered materials. The final product from Stage 2 is a liquid ammonium sulphate solution, which is concentrated and crystallized for sale into the fertilizer market.
Primobius enables customers to achieve high recovery rates for critical materials, supporting the circular economy and reducing reliance on mined resources. The hydrometallurgical process operates at low temperatures, minimizing energy consumption and emissions while delivering high-purity products that meet the demands of modern industries.
![]()
-
Graphical summary
![]()
High standards for safe, efficient recycling
Primobius establishes industry-leading standards enabling clients to operate battery recycling plants with superior safety and efficiency. Flexible and robust designs prioritize safety at every stage, addressing potential risks proactively from the outset. Old batteries are managed responsibly to mitigate the risk of fires and the release of hazardous substances. This comprehensive safety concept enhances environmental stewardship by reducing resource consumption, minimizing emissions, and promoting efficient, responsible recycling practices.
- Regulatory compliance: Our solutions adhere to rigorous regulations such as the EU battery directive, supporting safe and compliant operations.
- Fire safety: The wet shredding process significantly reduces fire hazards, and advanced fire detection systems manage fires by flooding enclosed areas with CO2.
- Operational efficiency: The design eliminates the need for full-body PPE and reduces dependencies on continuous consumables like nitrogen, streamlining processes.
- System reliability: The absence of a vacuum system reduces maintenance needs and minimizes risks such as nitrogen leakage, with no specific cleaning requirements.
- Environmental protection: Our off-gas system, featuring filtering and wet scrubbing, safeguards the environment from volatile organic compounds and dust.
- Resource conservation: Our water treatment solutions promote resource savings and support waste-water-free operations.
- Administrative ease: Easier permission procedures with authorities facilitate smooth operations for our clients.
Downloads
Contact
Have a question or would like to collaborate? Get in touch now.
-
Ulf Rademacher
-
Ulf Rademacher
Senior Business Development and Sales Manager
+49 2733 293998Primobius GmbH
Ohlerkirchweg 66
41069 Mönchengladbach
Germany![]()
-
Sushant Patro
-
Sushant Patro
Senior Business Development and Sales Manager
Primobius GmbH
Ohlerkirchweg 66
41069 Mönchengladbach
Germany![]()